Presented by: Dut Kim Sru
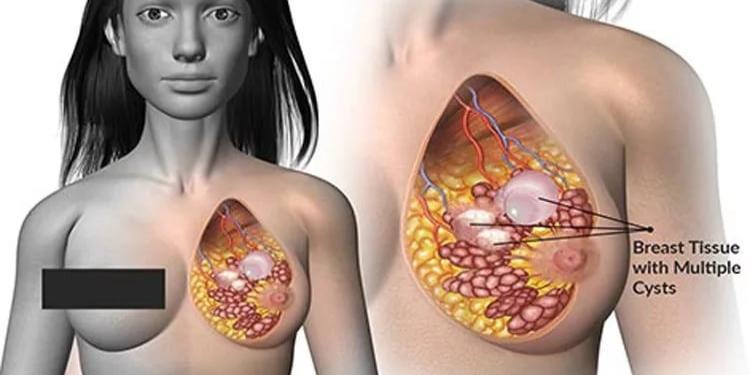
Breast cysts are round or elongated with water inside. About 25% of all breast cysts are cysts. Most breasts are benign and do not increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
The cyst is small or large enough that you can see under your skin or the image in the test (evidence of cysts). Many cysts are medium in size (neither large nor small).
Cysts can occur in people of all ages, but most often occur in women in their 40s. In more than half of all cases, women may develop multiple cysts at the same time or in stages. Use a cyst large enough to be felt, it is generally round and can appear under our skin. Cysts can cause pain, stress or roughness in the breasts. These signs may worsen or improve at different stages of the menstrual cycle.
Diagnosis of cysts:
When diagnosing a cyst, the doctor wants to know if the cyst is a normal, complex cyst or a cyst that is difficult to diagnose. Sound equipment is used to determine what type of cyst is present.
Simple cysts: smooth, thin, normal and only hydrated inside. The sound device can detect through the passage of sound on the disc, indicating that there is no solid growth inside. Normal cysts are benign.
Complex cysts: Irregular borders, thick neck, and lumps or lumps in the cyst. Sound passes back through the sound device. Complex cysts can sometimes be drained through needles so that the water inside can be tested. If abnormal blood or cells are present, further testing is needed to diagnose breast cancer.
Hard-to-diagnose cysts: Between normal and complex cysts. Although it resembles a normal cyst, it has some clots inside that show through the sound waves. However, this type of cyst does not have thick skin like complex cysts.
It should be noted that scholars research on the study of cysts use difficult to judge or complex each other. Therefore, if you come across any case, you should ask for specific information about that case. Most of these cysts are benign.
The cyst complex requires doctors to study whether the lumps inside contain cancer cells. In such cases a diagnosis is needed (details below).
Treatment and follow-up:
For normal cysts, no treatment is required, except for large, painful or painful cysts. Cysts can swell through needles. If the cyst returns, repeat the test using a mammography program and repeat the ultrasound with a needle. Most women have simple cysts that need to be checked for breast cancer on a regular basis.
For cysts that are difficult to diagnose or complicated (severe) need to be monitored as usual after confirmation is a cyst. In this case, your doctor will order you to pump with a needle and test the fluid inside. Doctors need to see and examine you every 6 to 12 months for 1 to 2 years. You usually have to go for a mammogram with or without mammography.If there is a suspicious case, your doctor will still test you for a benign cyst. Sometimes a doctor may prescribe an injection or remove a cyst.
Most women are worried about complicated cysts or cysts that are difficult to diagnose, but most cysts are okay. “I always tell women to think about what can happen if they leave a glass of water for months and the water will not be clear and dirty” by Dr. Stolier. “A similar process can often occur in cysts”If you have a lot of cysts or your cysts develop frequently, you can see a breast specialist. Having breast cancer, along with other cancer risk factors such as heredity, can cause most women to do just that. Although cysts do not increase the risk of cancer, having a breast specialist can reduce your anxiety.
Source: Translated from the website of the Breast Cancer Organization